By clicking “Accept”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts. View our Privacy Policy for more information.
25 Must-Have Pages for Your Ecommerce Website
What pages make up an ecommerce website?
The most essential ones that come to mind are home page, product page, shopping cart, and checkout.
But there’s more to an ecommerce website than these.
Over the years of designing ecommerce websites, we put together a master site map of every must-have page that should be included in an ecommerce website. We identified 25 pages that we believe are very important for any ecommerce website to include.
Here are the 25 most important pages for your ecommerce website:
- Homepage
- Category Overview
- Category Page
- Product Page
- Search and Listing Results
- Login/Create Account
- Mini Cart
- Cart Page
- Log In/Guest Checkout
- Shipping
- Payment
- Checkout Review
- Order Confirmation
- Orders/Order History
- Individual Order View
- Profile/Account Settings
- Payment Settings
- Addresses
- Email & SMS Sign Up
- Returns
- Shipping
- Help/Contact Us
- Store Locator
- Store Details Page
- Terms and Conditions/Privacy Policy

General Ecommerce Pages
1. Homepage
The homepage is important, no question about that. It’s often the first impression a brand gets to make, and usually the first page to tackle in an ecommerce design.
The homepage can include promotions, branded lifestyle imagery, and featured products or categories. Value propositions should be clear, like what makes the brand or products unique, and any brand guarantees such as free shipping should be highlighted.
While the homepage is regarded as the front door of the site, keep in mind that people don’t always enter through the homepage and may arrive via direct links to other pages.
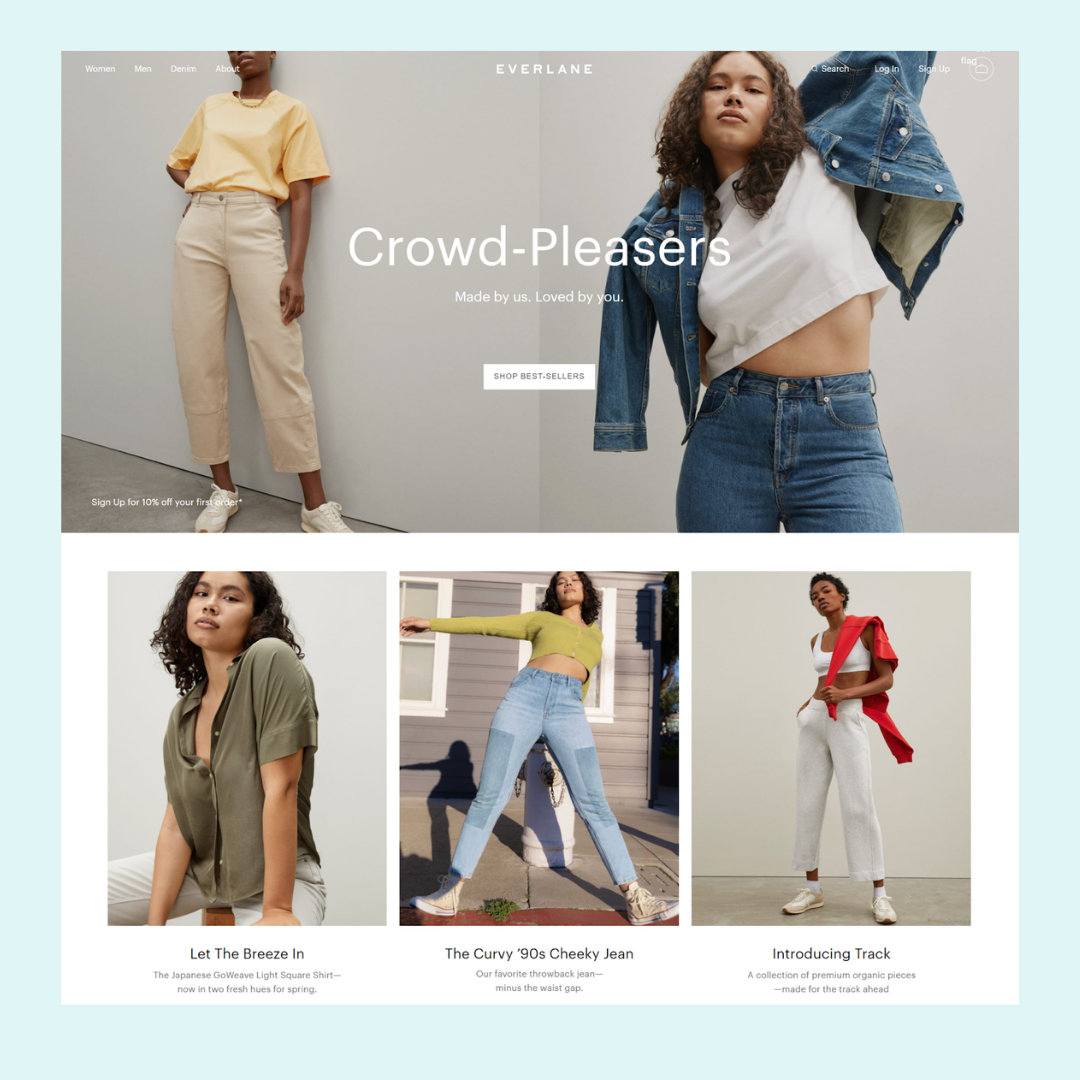

2. Category Overview
This refers to the landing page for a top level category, such as Women or Electronics, which displays an overview of what’s within that category rather than list all the products.
Multiple Category Overview pages may be used if there are more than two levels, such as Women's > Tops > Sweaters.
However, if your categories are only one level deep, you can skip the Category Overview page and go straight to the Category page.
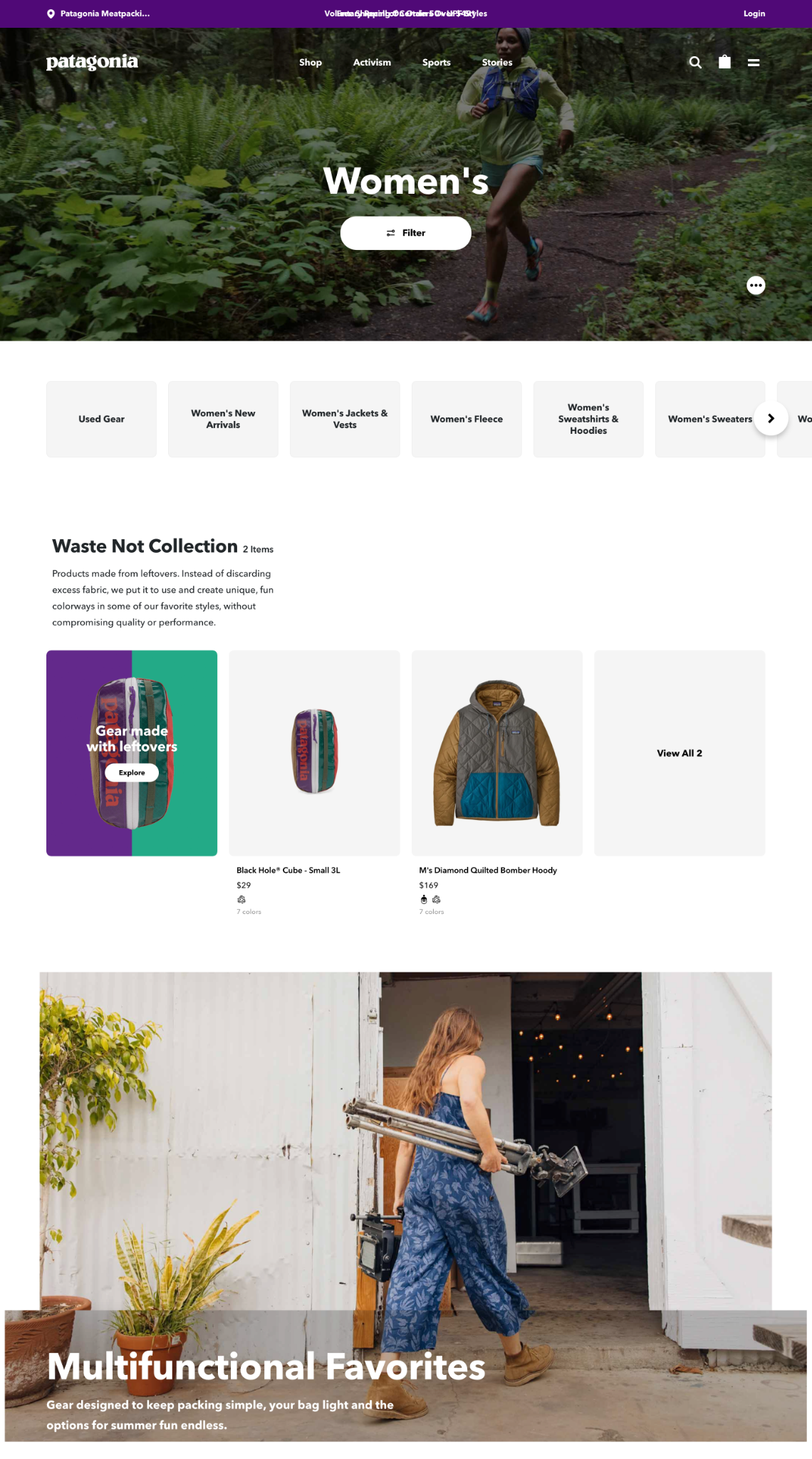

3. Category Page
The Category page is the list view of products for a specific category or subcategory, usually displayed in a grid layout. It often includes filters so the user can drill down and find what they are looking for.
The focus of this page is for the user to browse and see a lot of products at once, compared to the Category Overview which focuses on promotion and wayfinding.


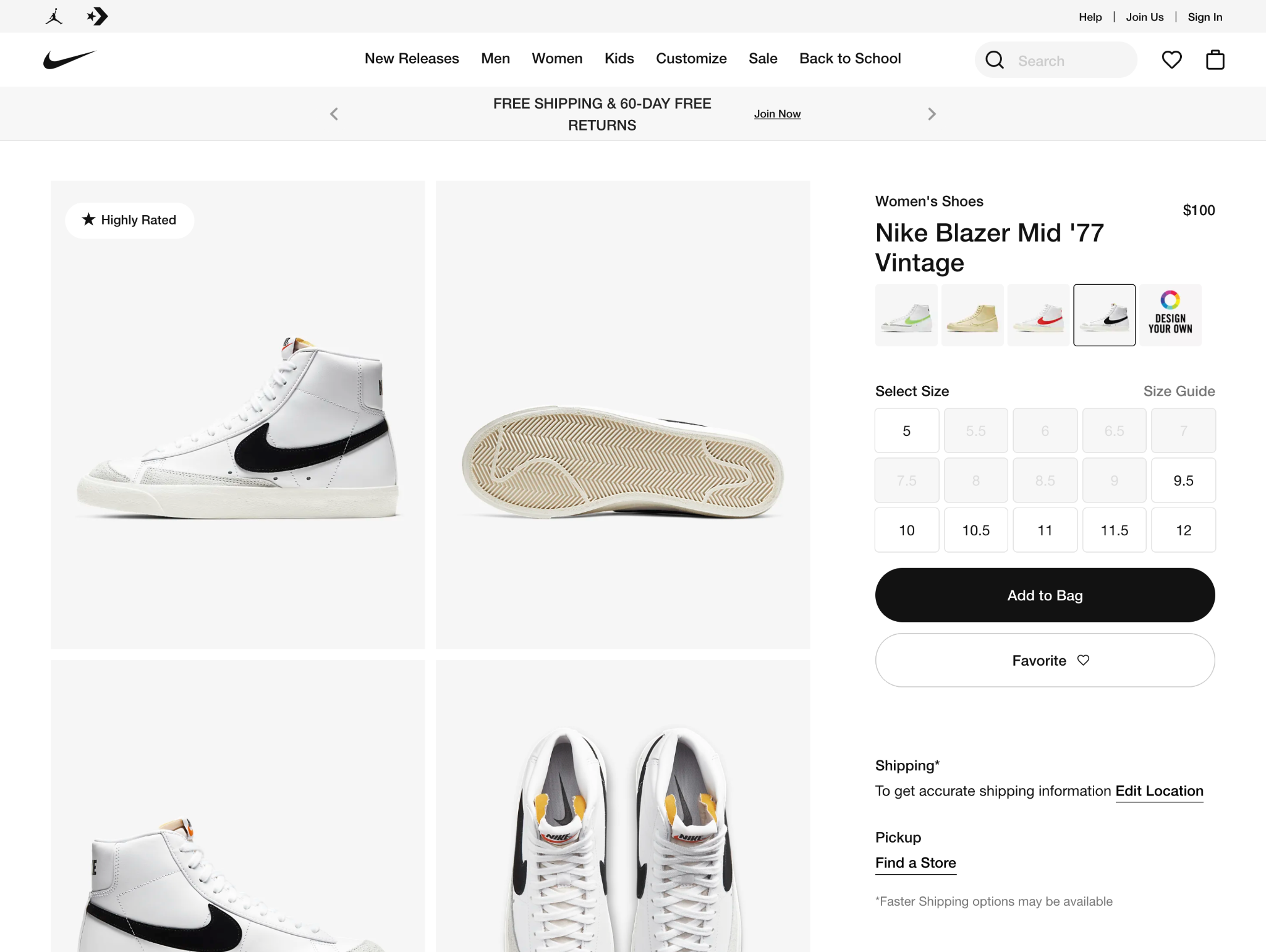
4. Product Page
Sometimes referred to as the Product Detail Page, this is the individual view of a product with the full product details and pricing. The main call to action is the add-to-cart button.
Adding reviews, related products, and user-generated content from social media to this page can help drive customers to add-to-cart.

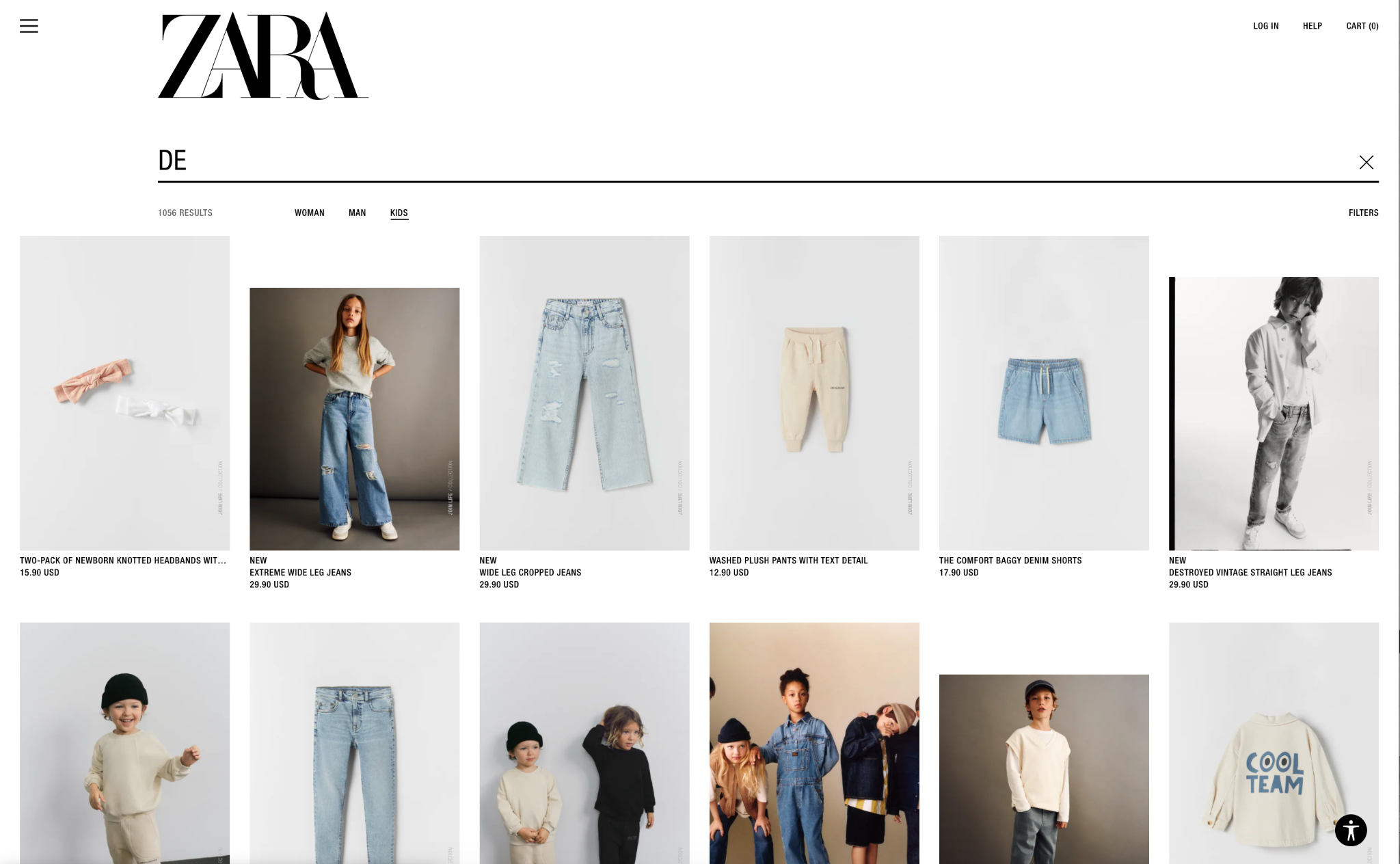
5. Search and Search Results
Ecommerce sites should have search functionality, especially for sites with a wide range of products. The search field is usually located in the navigation menu.
Make sure to consider how the Results page displays the results. This page often follows the Category Page template, or it could have its own unique design. Implementing ‘suggested search’ surfaces products while the customer is typing to remove the need to go to a dedicated search results page.

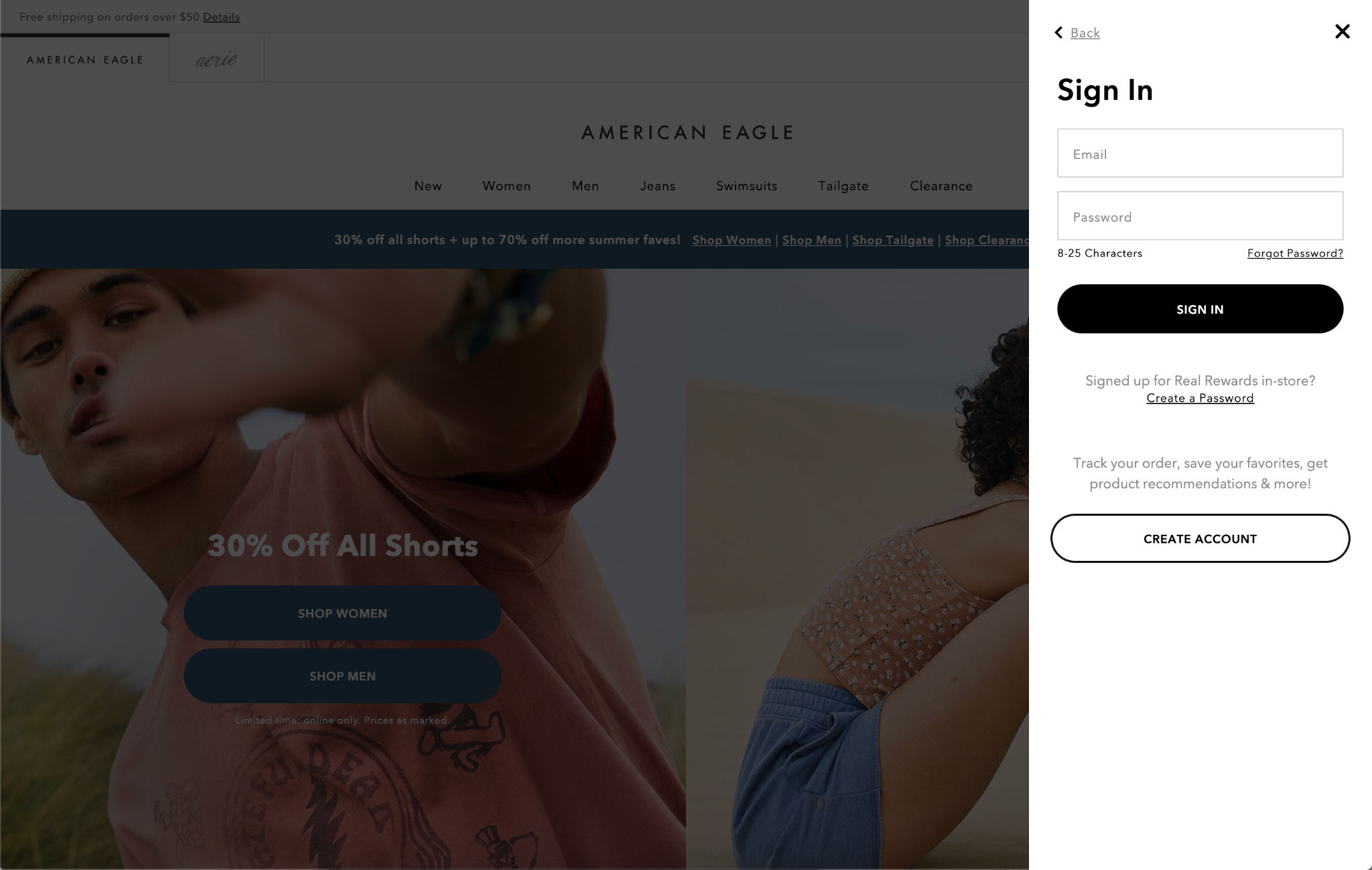
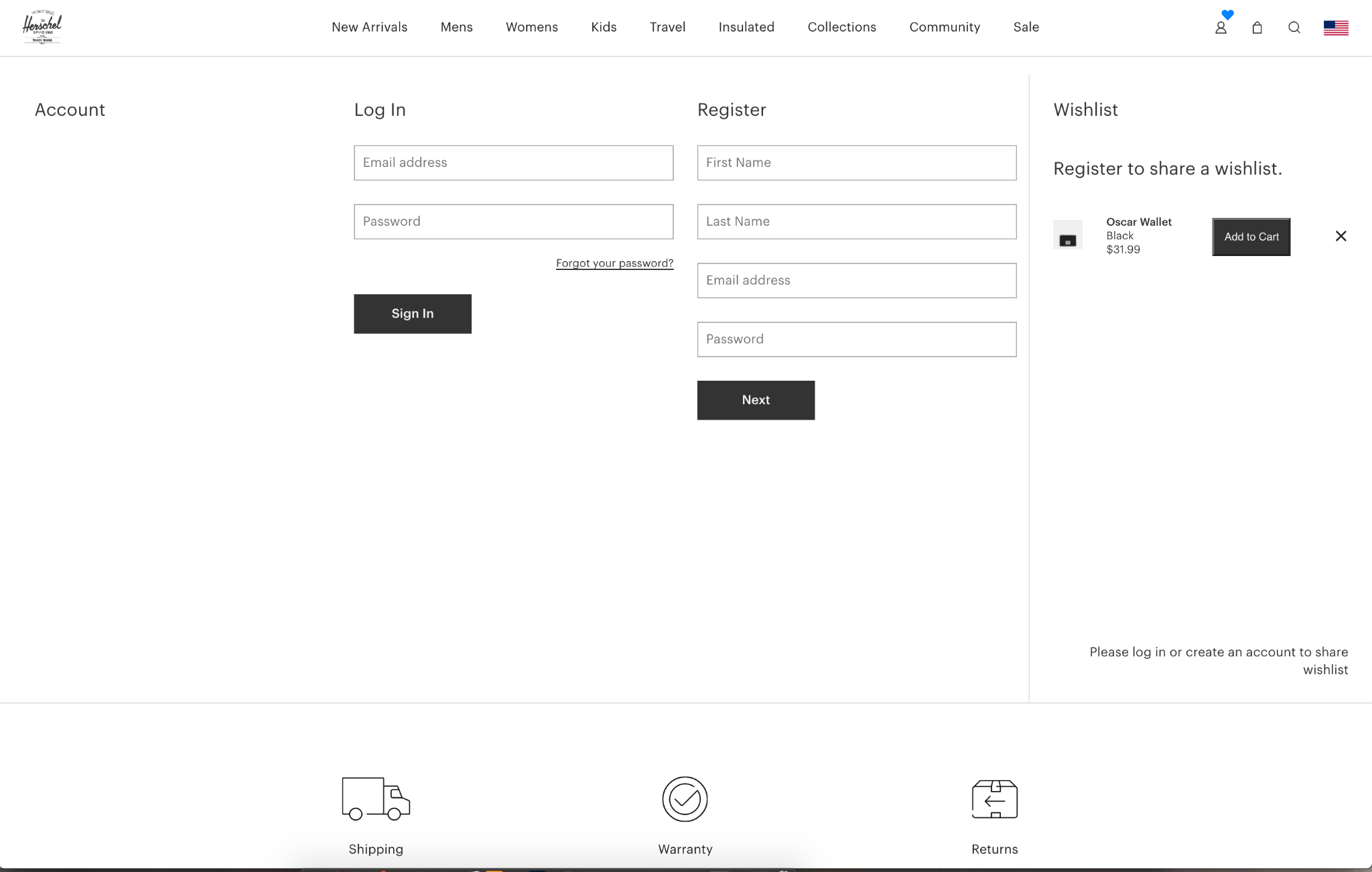
6. Login/Create Account
Ecommerce sites with account functionality allow customers to save data such as order history and payment information and can enable other interactions such as wish list management, the accrual of rewards/loyalty points, and special access to deals.
The login/create account form can live on its own page or be treated as a modal or dropdown. Make sure creating an account is accessible from the login fields (and vice versa), so when a user realizes they don’t have a login they can easily get to Create Account.
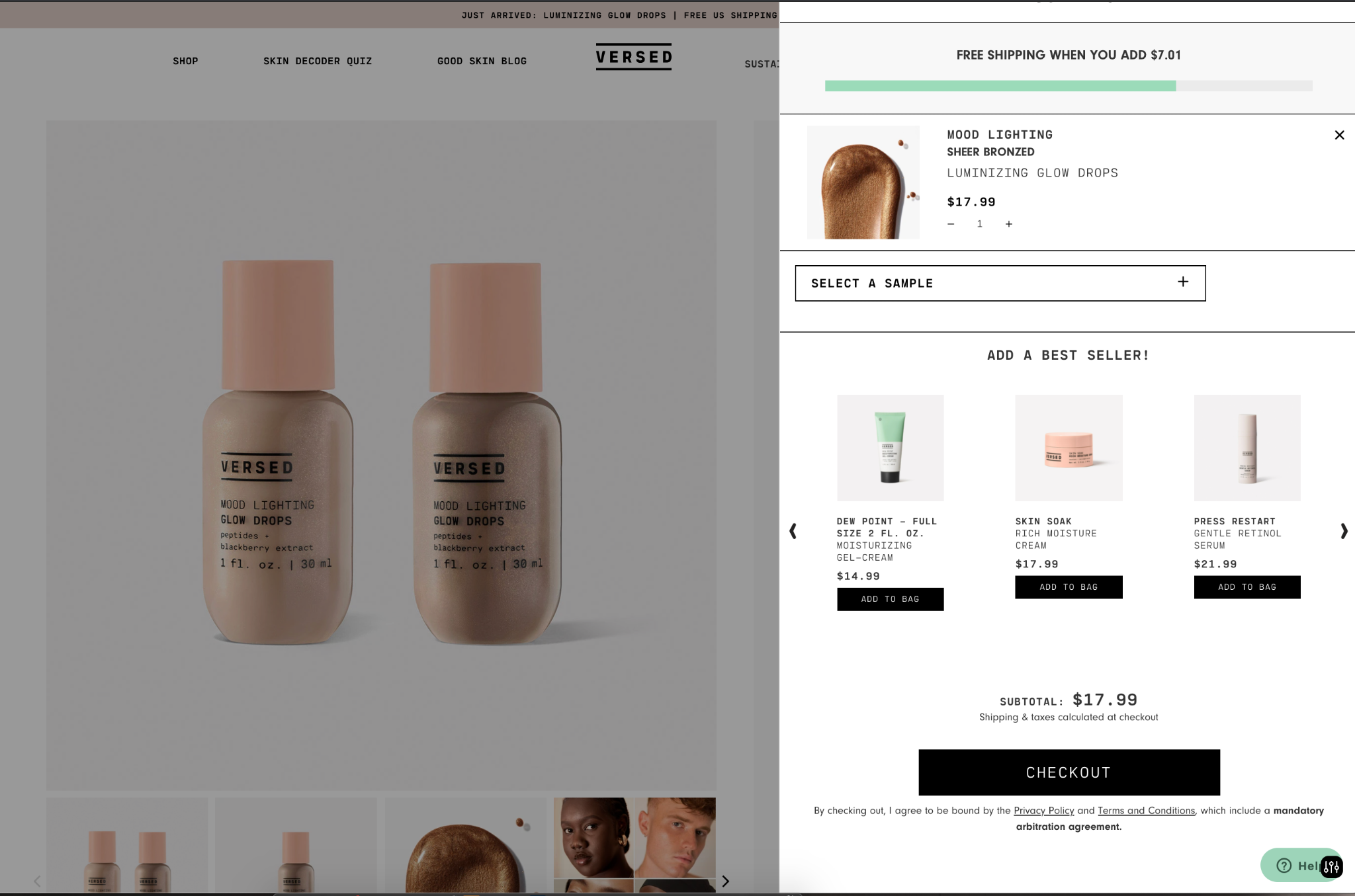
7. Mini Cart
The ‘mini cart’ is technically not a page, but it’s a must-have view to include in your ecommerce site. It’s important to provide visual feedback when the user adds an item to their cart, and the mini cart does just that.
The mini cart is often in the form of a dropdown or flyout coming from the cart icon in the nav, or a modal on the page. Keep it informative by recapping what was added and update the cart subtotal.
This is also a great opportunity to get the user to keep shopping by showing how close they are to free shipping and presenting related products.


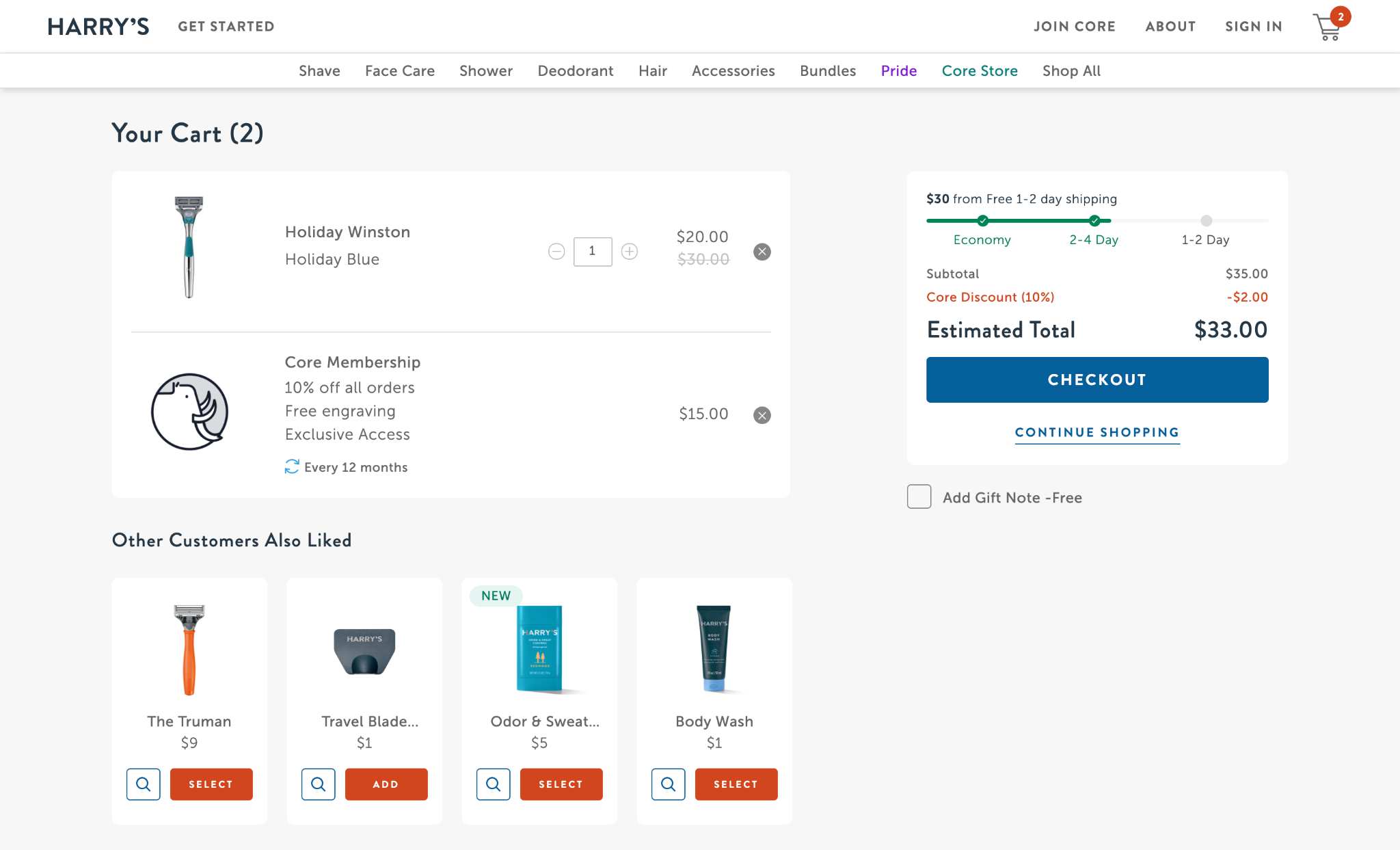
8. Cart Page
The shopping cart needs to list everything the user has added and have the ability for the user to make changes.
It’s good practice to show estimated shipping cost and the promo code field at this point so the user can get a good idea of their final cost without going too deep into the checkout process (for shipping estimates to work, the user may have to input their zip code in advance).
You don’t want abandonments to happen on the last step of the checkout when customers discover the cost of taxes and shipping, and that their promo code doesn’t work–it’s frustrating for both the store and the customer.
The cart page can also be an opportunity to upsell related products.

The Checkout Flow:
The following pages for the checkout flow are some of the most critical must-haves in an ecommerce site, as these pages are where the conversion (the sale!) happens.
9. Log In/Guest Checkout
After a user reviews their cart is the perfect moment to prompt the user to log in (if not already logged in) for a quicker checkout experience by using saved information.
The user may not want to deal with creating an account or remembering their password, so provide the ability to checkout as a guest, which will require them to fill out all their information.


10. Shipping
The shipping page within the checkout should include the form fields needed to gather shipping address. There’s often a checkbox to use the same shipping address for the billing address.
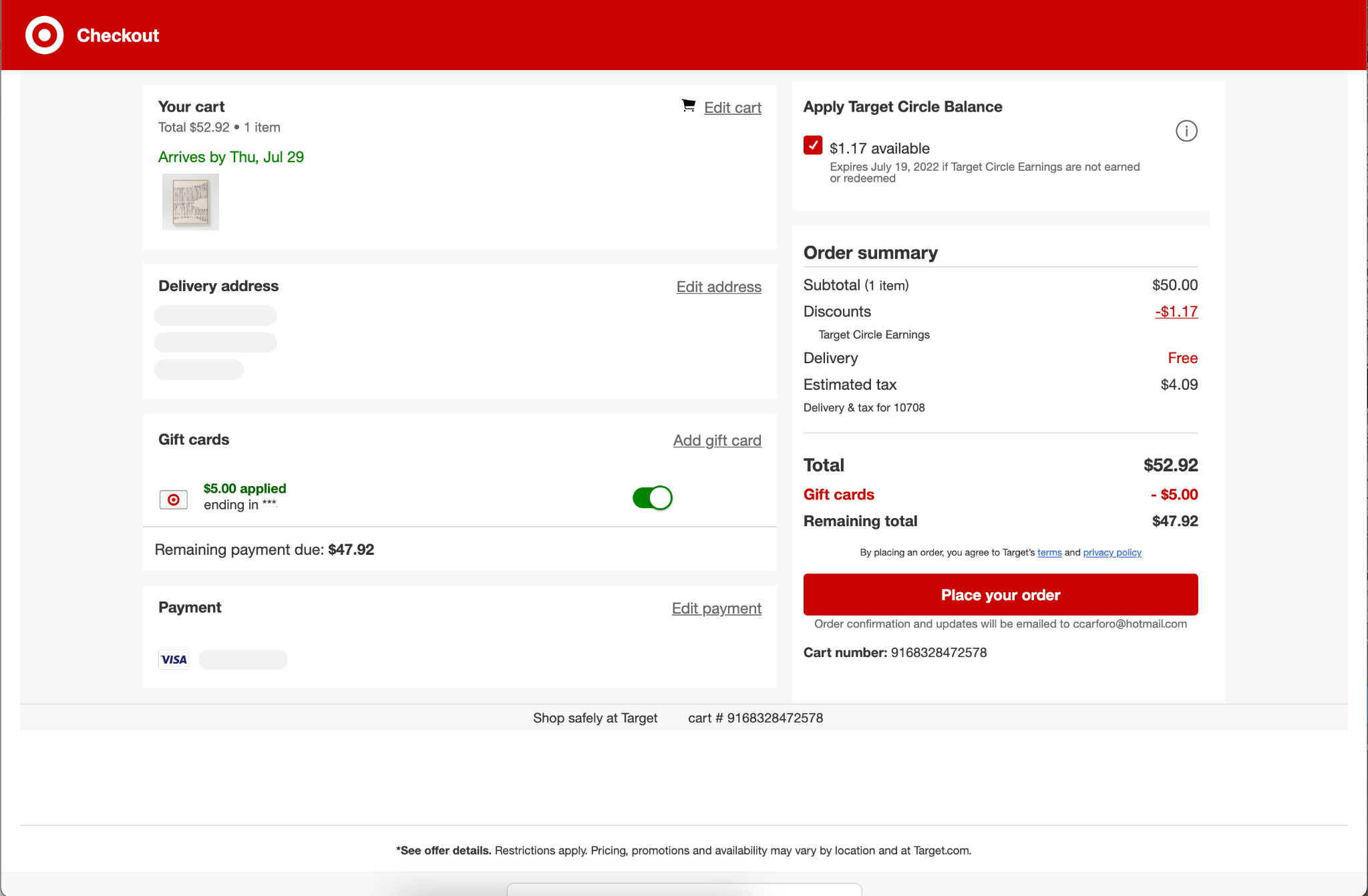
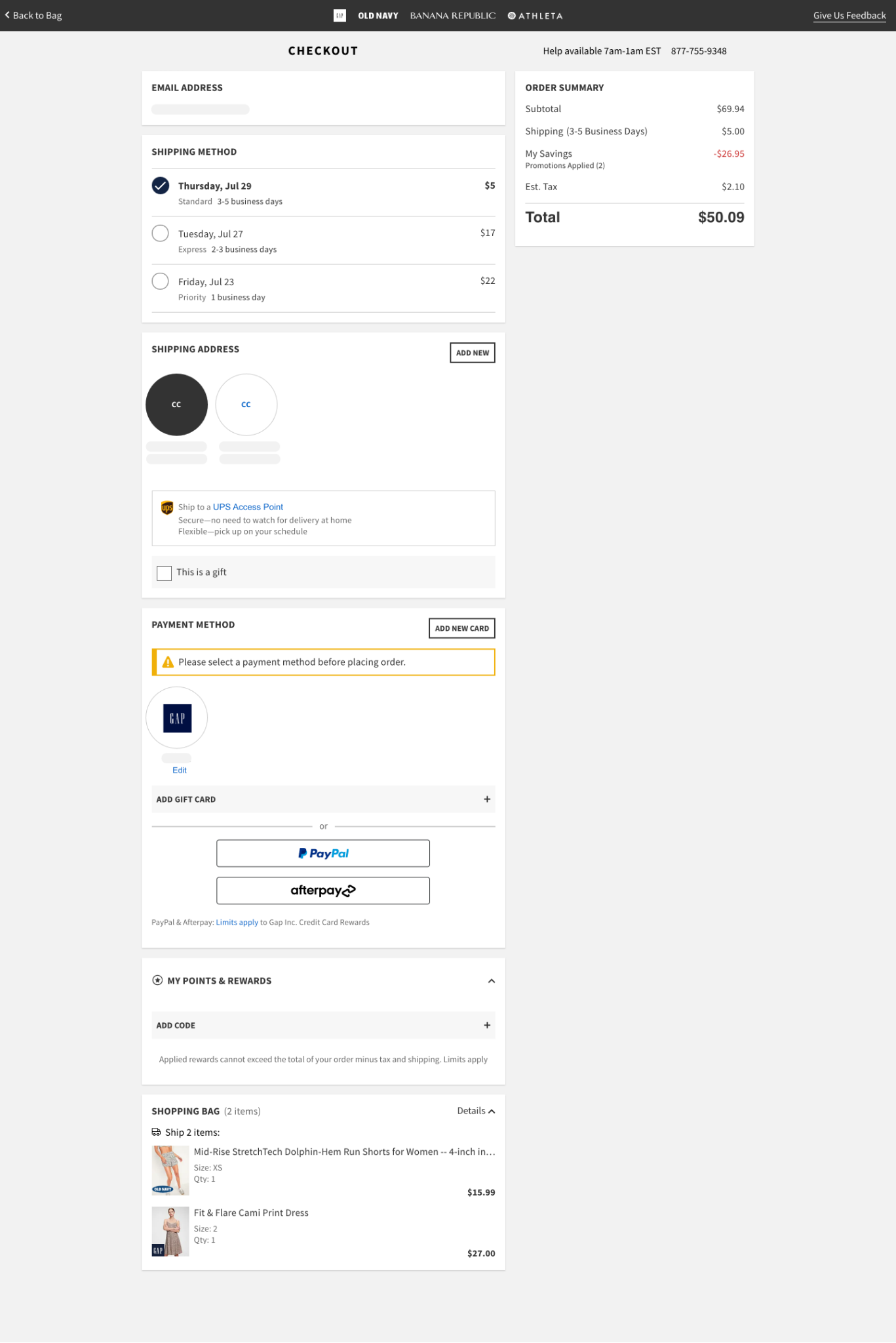
11. Payment
The payment step includes form fields to input payment information. This may include fields to enter a billing address, especially if it’s different from the shipping address.
This step can also include the option to enter gift cards, rewards points, or promo codes, or pay with rewards points or store credit.
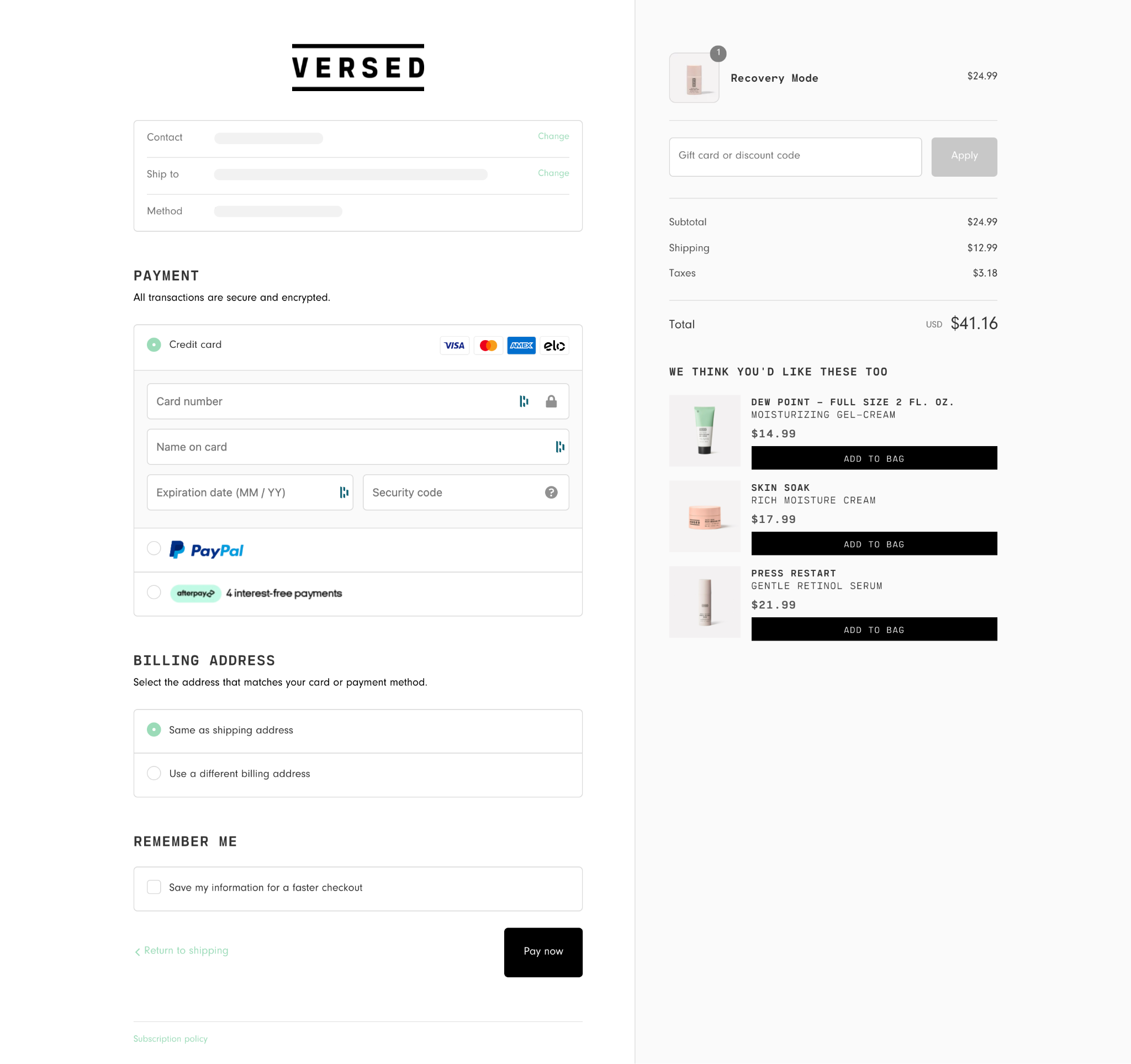
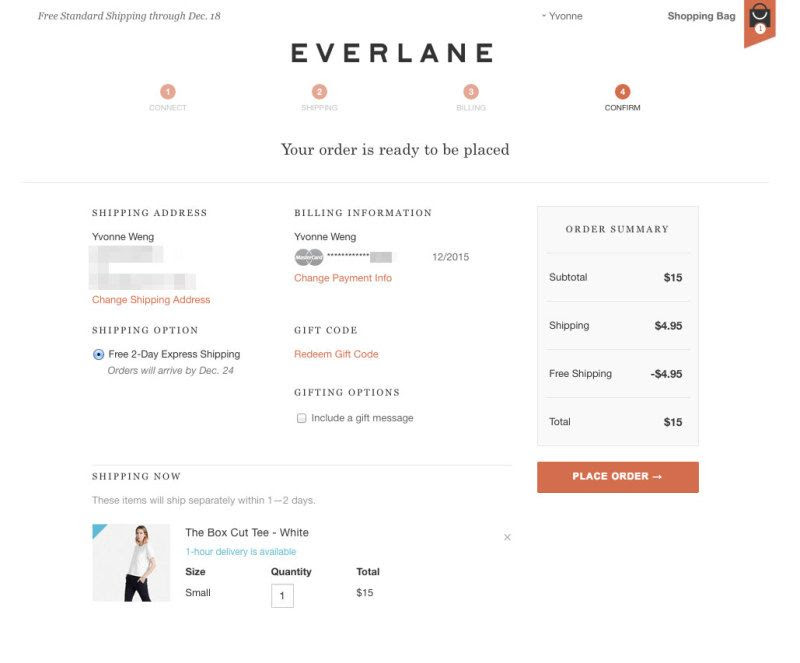
12. Checkout Review
This is an important step to review all items being purchased, the shipping info, payment method, discounts, and extra costs like taxes or express shipping.
Make sure it’s clear that this is a review step and that the main call to action is to submit the order.
13. Order Confirmation
Once the customer submits the order, give them a nice thank you message and confirm that they submitted their order successfully. It’s helpful to display the order details and info on how to modify the order if the user catches a mistake after submission.
If this was a guest checkout, take the opportunity to prompt the user to create an account to save all the information that they just submitted.
Confirmation pages may be used to display a message other than a thank you. As the system processes the order, something could go wrong and the site will need to return an error page instead of a confirmation to explain that an item sold out by the time the order was submitted.

Account Pages:
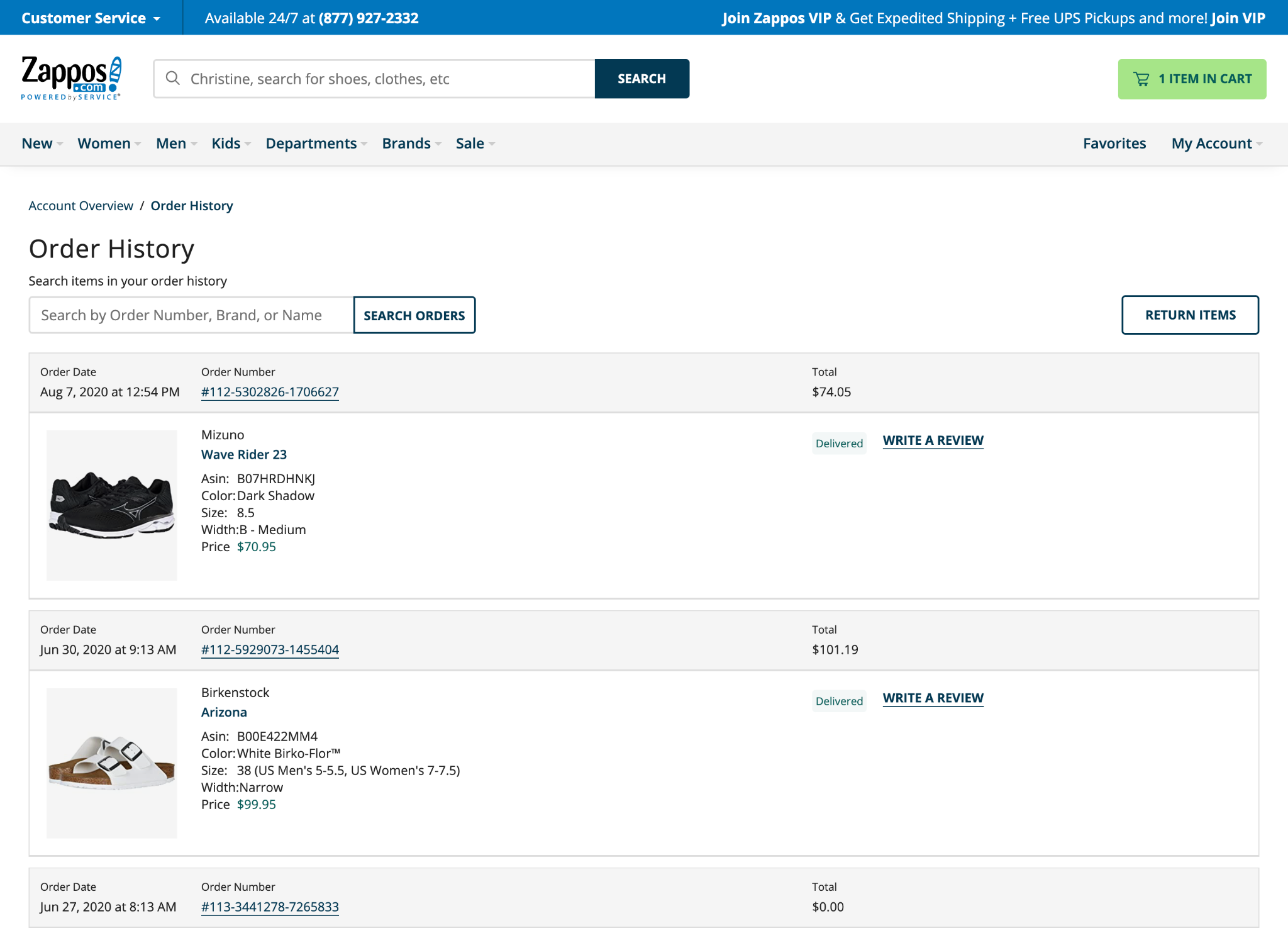
14. My Orders / Order History
The Orders page lists any current orders as well as all past orders so the user can reference previous purchases.
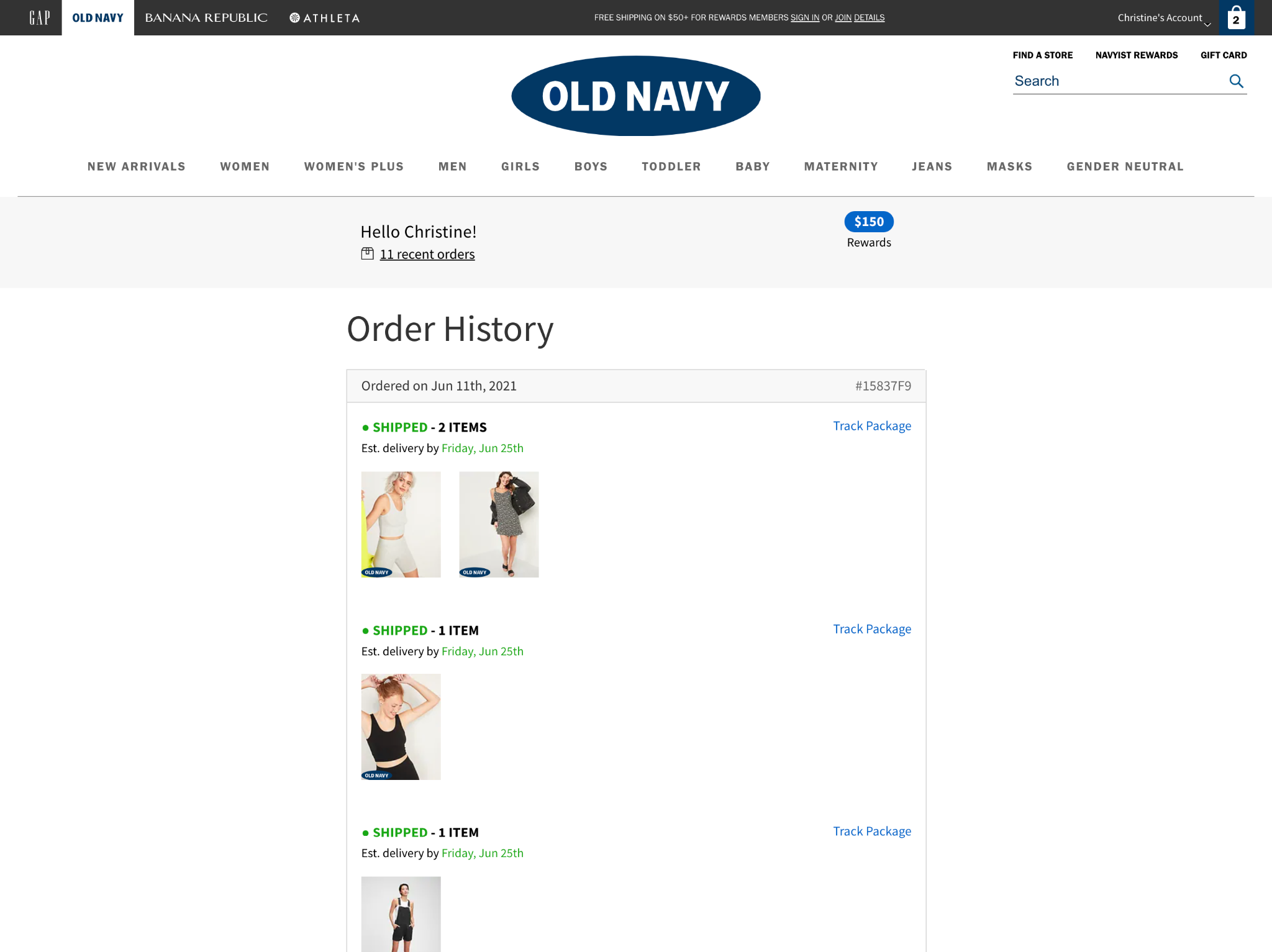
15. Individual Order View
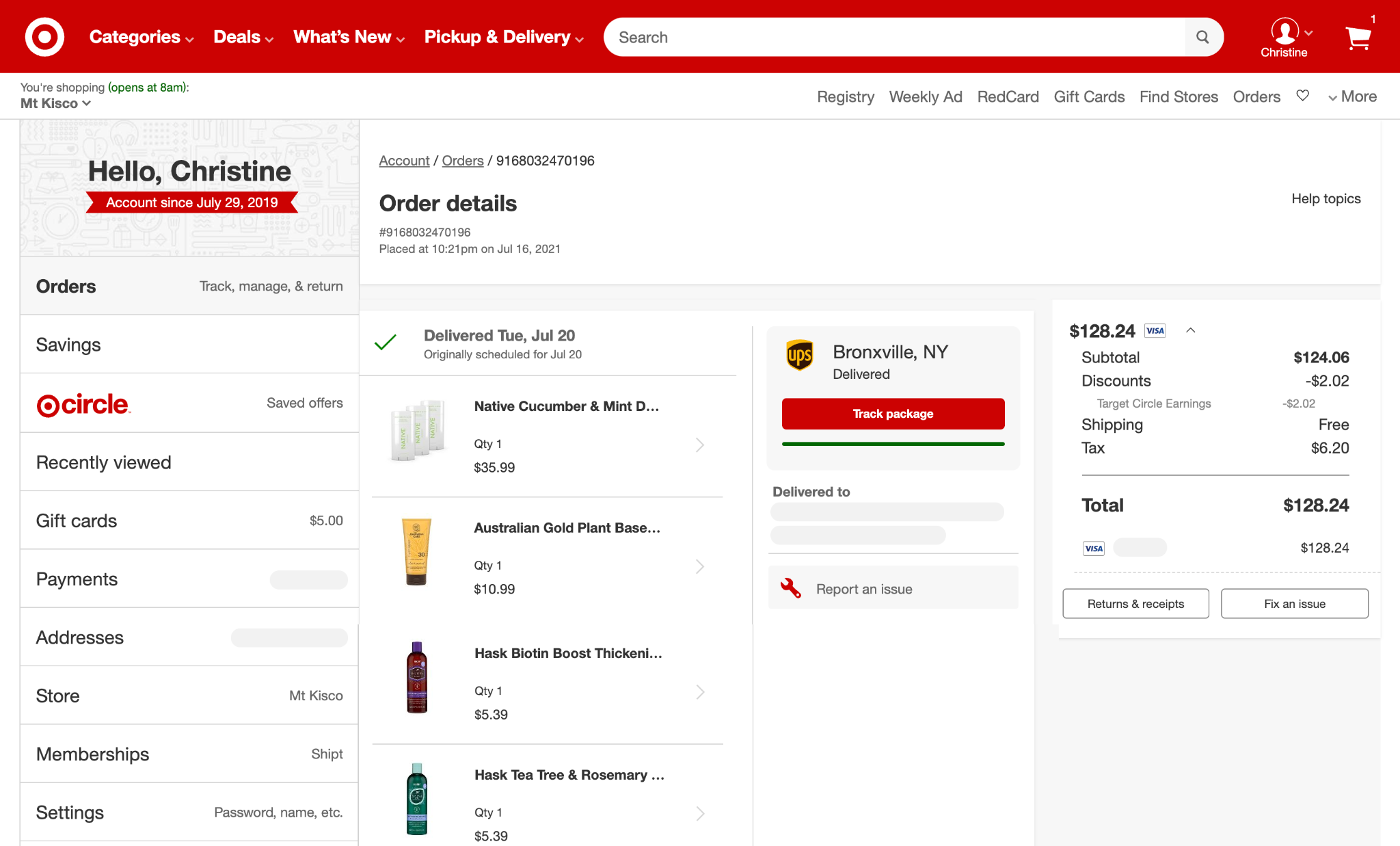
This page is like the receipt for a given order. It should include full details for that order – from what they bought to where it got shipped to. Depending on the sophistication of the ecommerce platform and its integration with shipping/fulfillment software, a tracking number may also be included with each order.
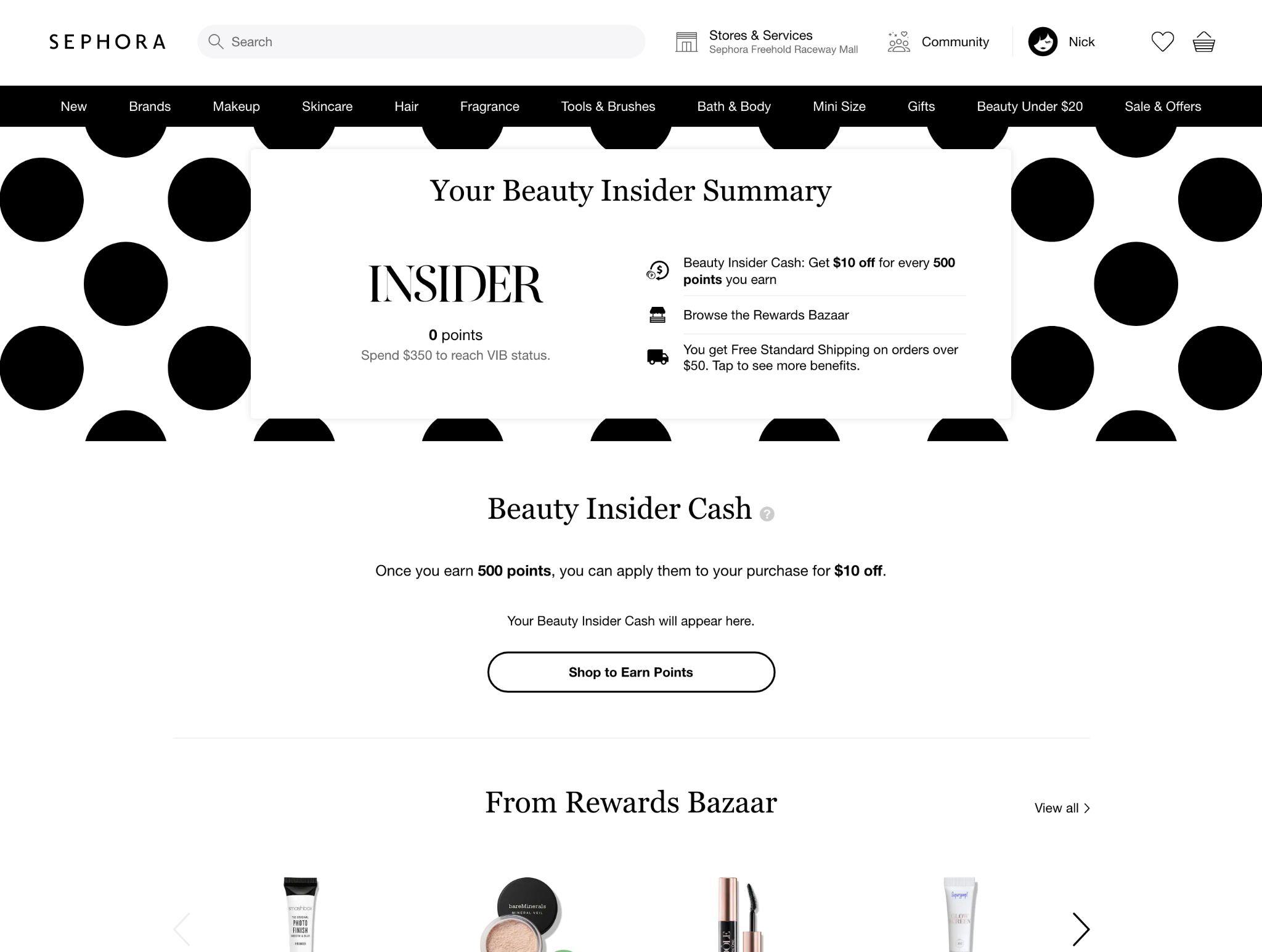
16. My Profile / Account Settings
Whether it’s labeled as “My Profile,” “My Settings,” “Account Information,” and so forth, this page includes all the basic account fields, such as name, email, and change password details. It’s common to include any additional information that’s collected from the user, such as demographic information.
The customer’s account is also a great place to offer them access to their saved Wishlist items. Most companies incentivize account sign ups by only allowing a customer to save an item to a wishlist if they have an account.
Rewards and loyalty program details can also live within the profile page, allowing customers to see their rewards balance, learn how to earn, and apply their rewards to their order.
17. Payment Settings
The Payment Settings (or Manage Payment) page lists saved payment info (gathered from previous orders), and gives customers the ability to update or delete that information.


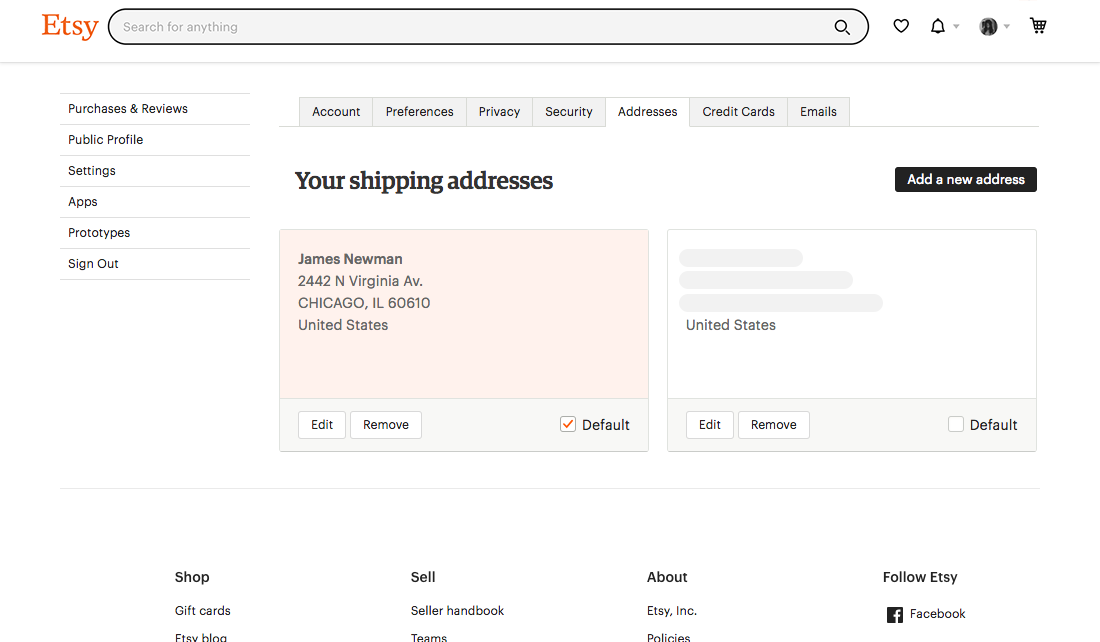
18. Addresses
The Addresses page lists saved shipping addresses (also gathered from previous orders), with the ability to update or delete.
Footer and Content Pages:
19. Email & SMS Sign up
Email and SMS are critical lifelines of ecommerce. It’s a sure way to guarantee return customers and market to interested prospective customers.
Ecommerce sites should make it easy for interested visitors to sign up. This doesn’t have to be a dedicated page – you can opt for a simple field in the footer or a pop-up modal. Provide an incentive for signing up, like a free shipping discount, and give a short overview of what type of emails they’ll be getting.
Don’t forget to consider the confirmation message that comes after submission. This, too, can be its own page or load into the modal/footer area.


20. Returns
Returns are an important part of shopping online, which is why there should always be a clear link to the returns page in the footer. This page should also be accessible during the checkout flow, as cart abandonment may happen when a user is unsure about the return policy and can’t confidently complete their purchase.
The best return pages lay out the return/exchange process in an easy-to-understand way while addressing common questions and concerns.

21. Shipping
A big question on online shoppers’ minds is the shipping time and cost, so an easy-to-find shipping information page (often in the footer, like returns) is essential. Include information about international shipping policies and any special holiday shipping schedules.

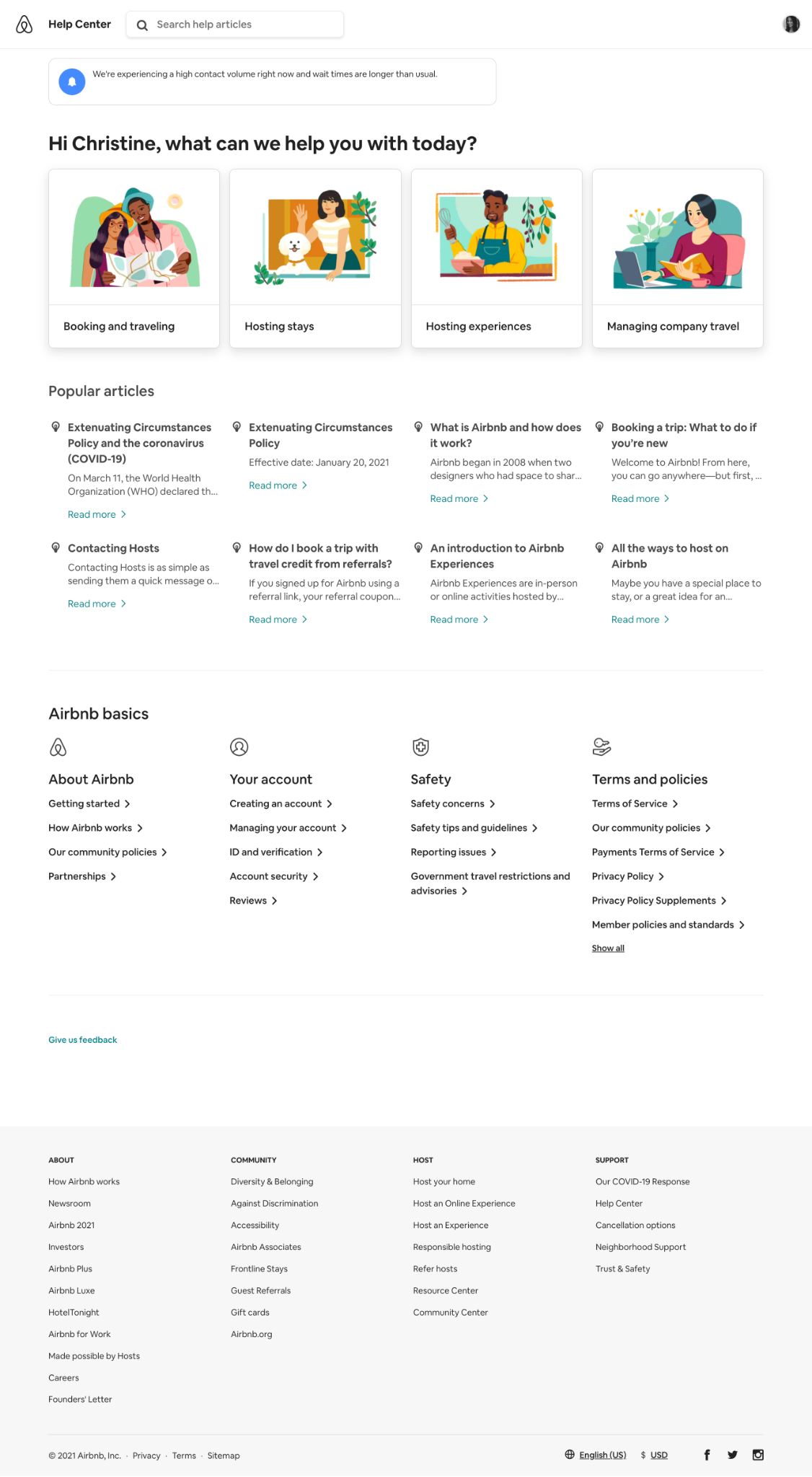
22. Help / Contact Us
Give your customers a centralized place to find ways to get in touch with customer support whether with an email address, phone number, form, or live chat with a Help or Contact Us page. Many sites combine FAQs with Contact Us to provide answers to questions that may have come up many times in the past (and also to save time).
Don’t underestimate the importance of the Contact Us page – customer service is a huge driver for business growth, and making customer service accessible and easy will provide a superior experience to users and get people to spread the word about the store and brand.

23. Store Locator / Where to Buy
When you have physical store locations, some visitors will come to the site for the sole purpose of finding a store near them. Likewise, if your brand doesn’t have its own physical store but its products are sold by other retailers, it’s important to provide a page for users to find who stocks the brand and where they can go buy it.


24. Store Details page
As you drill down from the Store Locator page, provide full details about a particular store, like a map and business hours.

25. Terms and Conditions, Privacy Policy, and Web Accessibility Policy
As with all sites, don’t forget to include the legalese.

If your site is compliant, it is important to include an accessibility statement, which services as an acknowledgement and commitment of accessibility, provides customers information about the accessibility of the company’s content, and shows customers that your business cards about them.

The above list covers everything that’s needed on a core level, but an ecommerce site may need much more based on the type of products it sells and the unique goals of the brand and the store.
Consider other pages and features like the About page, Blog, Wish Lists, Careers page, and more.
Posted on
August 30, 2021
Interested in collaborating on a project?
Get StartedLatest Updates

Launching a New, Premium Ready-To-Drink Vodka Cocktail
News

Easier Navigation for Once Upon a Farm’s Growing Product Catalog
News

Reimagining Luxury Eco-Hospitality With Few & Far
News

Launching a Line of Luxury Skincare Products Laser-Focused on Hydration
News

Creating a Tailored Experience for Rentacrate’s Customers
News

Reactor Unveils a Futuristic Website for Sci-Fi Enthusiasts
News

A Fresh Perspective for Well+Good
News

Merging Sustainability and Luxury With Encore Bag
News


